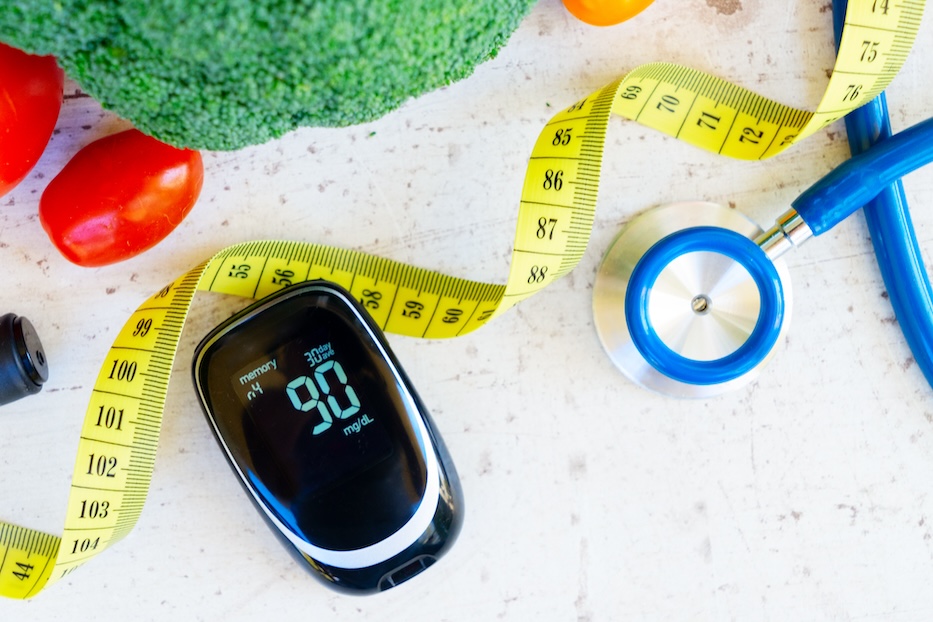
Diabetes is a condition increasingly affecting many people in Canada and globally. Fortunately, with the guidance of a dietitian-nutritionist, this condition can be effectively managed. In this article, we'll explore practical and balanced tips for maintaining stable blood sugar levels, avoiding restrictive diets, and embracing intuitive, balanced eating.
1. Understanding the Role of Diet in Diabetes Management
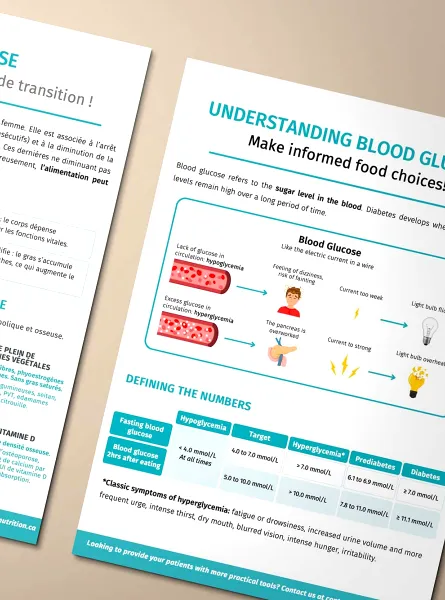
Diabetes, whether Type 1 or 2, is characterized by high blood sugar levels (Diabetes Quebec, 2021). Diet plays a key role in regulating these levels. A balanced approach, overseen by a dietitian or nutritionist, can help control blood glucose while fostering a healthy relationship with food.
The Importance of Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, legumes, and fruits, are crucial in a balanced diet. They provide a slow and steady release of glucose, unlike simple carbohydrates that can cause blood sugar spikes (Canadian Diabetes Association, 2022).
Dietary Fibers: Your Allies
Fibers, found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, slow down the absorption of glucose (sugar) into the bloodstream. This helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day (National Institute of Public Health, 2020). Here are different ways to increase your fiber intake: make meal salads, choose high-fiber cereal products for your classic recipes, or even incorporate legumes into your soups.
Proteins and Healthy Fats
Foods rich in proteins and good fats do not raise blood sugar levels. Instead, they help keep it stable. Eating these foods can also help you feel full longer, which can reduce the urge to snack between meals and help you better control your weight (Diabetes Québec, 2018). Additionally, they help prevent hypoglycemia in those at risk. It's recommended to consume a protein source at each of the three daily meals, at a minimum. Options like nuts, seeds, fish, and avocados are preferable (Health Canada, 2021).
2. Meal Planning: A Key Tool
Meal planning plays a crucial role in diabetes management. A nutritionist can help you develop a meal plan tailored to your needs and lifestyle.
Consistency in Meal Times
Eating at regular intervals helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. It also allows you to better listen to your hunger and satiety cues, thus avoiding overeating or undereating. It's recommended to add snacks between meals if the interval is more than 4 to 6 hours.
Portion Size
Understanding and adhering to recommended portions is crucial. A nutritionist can help you balance your meals intuitively while considering the amount of carbohydrates to consume according to your medication. For those with Type 1 diabetes, it is essential to calculate carbohydrates to manage the appropriate insulin dose for each meal properly. For Type 2 diabetes, carbohydrate counting can be done using visual cues.
3. Physical Exercise: A Complement to Diet
Regular physical activity is another crucial pillar in diabetes management. It helps regulate blood sugar and maintain a healthy weight. Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine is also beneficial for your overall well-being (University of Montreal, 2021).
4. Listening to Your Body
Intuitive eating is an approach that encourages listening to and respecting your body's hunger and fullness signals. This can be particularly helpful for people with diabetes, as it helps avoid restrictive diets and promotes a healthy relationship with food.
Managing diabetes requires a balanced and personalized approach. By working with a nutritionist, you can learn to balance your diet intuitively and effectively. If you're looking for help in managing your diabetes through balanced eating, make an appointment with a dietitian at TeamNutrition. Together, we can work towards achieving your health goals in a sustainable and healthy way.
References
- Canadian Diabetes Association. (2022). Diabetes management.
- Diabetes Québec. (2021). What is diabetes? https://www.diabete.qc.ca/en/diabetes/information-on-diabetes/what-is-d…
- Diabetes Québec. (2018). Proteins and diabetes management. https://www.diabete.qc.ca/en/diabetes/diabetes-management/diet/proteins/
- Health Canada. (2021). Canadian food guide for healthy eating.
- National Institute of Public Health. (2020). The importance of fibers in the diet.
- University of Montreal. (2021). Physical exercise and diabetes.