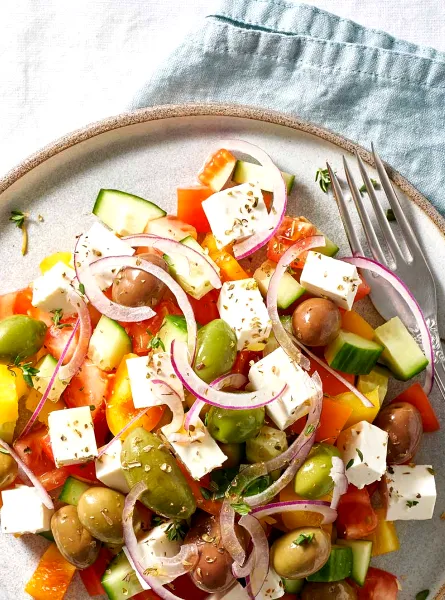Diabetes: A Chronic Condition Affecting Canadians
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting 9% of the Canadian population—nearly 1 in 10 people—and this number is expected to rise to 12% by 2025. The condition is characterized by a deficiency or dysfunction in insulin production, a hormone made by the pancreas. A lack of insulin leads to high blood sugar (hyperglycaemia), where sugar cannot enter the cells to provide energy. Over time, this can lead to complications involving the nerves, eyes, kidneys, and heart. Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90% of all cases, occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it.
The Benefits of Lifestyle Changes
Good news! Lifestyle changes can significantly help manage type 2 diabetes and may reduce or even eliminate the need for insulin injections. For type 1 diabetes, which affects 1 in 10 people with diabetes, insulin injections are required for life. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can improve disease management and help prevent complications.
Daily Tips for Managing Diabetes
1. Follow a Balanced Plate
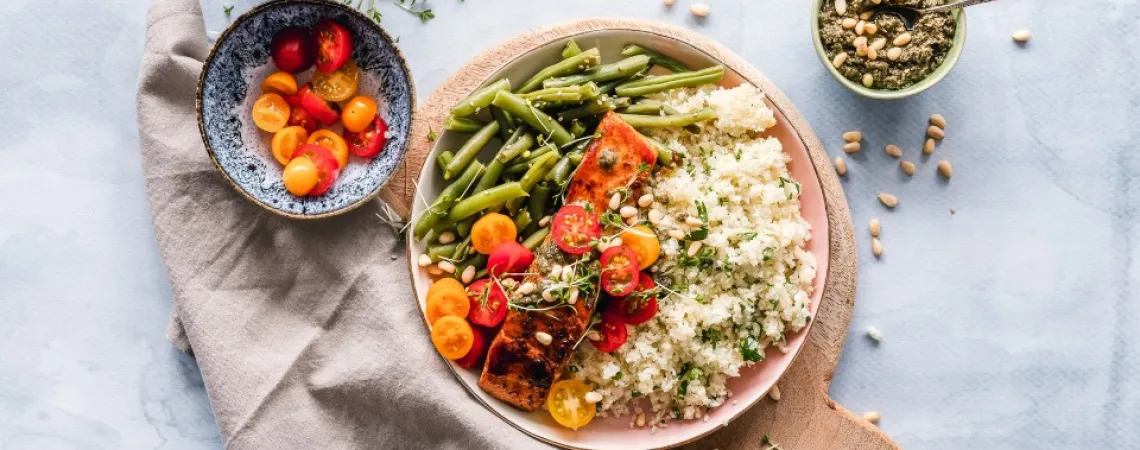
Building each meal based on the balanced plate model helps manage carbohydrates, which are key to controlling blood sugar levels. Divide your plate into:
-
½ colourful vegetables (high in fibre)
-
¼ whole grain starches (for slower sugar absorption)
-
¼ lean protein (to stabilize energy)
Practical tip: Use a plate divided visually to guide your meals. Learn to identify carbohydrate portions (e.g., ½ cup of brown rice = 1 serving).
2. Eat at Regular Times
Sticking to an eating routine with meals spaced 4 to 6 hours apart helps stabilize blood sugar levels and prevents sharp rises or drops.
Practical tip: Set phone reminders for your meals. Keep a healthy snack on hand in case a meal gets delayed.
3. Be Physically Active
Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and supports better blood sugar management. Aim for at least 30 minutes of movement, 5 days per week.
Practical tip: Start with daily walks after meals. Use a pedometer or smartwatch to track your progress. Mix up activities to stay motivated (e.g., swimming, cycling, dancing).
4. Choose High-Fibre Foods
Fibre slows carbohydrate digestion, helping avoid blood sugar spikes. It also promotes fullness and gut health.
Practical tip: Add 1 tbsp of chia or ground flaxseed to your meals, swap white bread for whole grain, and include legumes (lentils, chickpeas) at least 3 times per week.
5. Prioritise Water
Water is the best hydration option that doesn’t affect blood sugar. Sugary drinks should be avoided as they cause rapid spikes in blood glucose.
Practical tip: Always carry a reusable water bottle. Add lemon or cucumber slices to make it more appealing.
6. Reduce Intake of Sugary Foods
Highly sweetened foods can spike blood sugar levels quickly. Enjoy them occasionally, in small portions, and preferably with a balanced meal to lessen the impact.
Practical tip: Save desserts for when you’re already having a well-balanced meal. Opt for homemade versions with less sugar or enjoy fresh fruit to satisfy sweet cravings.
7. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can disrupt blood sugar levels, especially if consumed without food. It’s safer to drink alongside meals.
Practical tip: If you drink, choose a glass of wine or light beer with a meal, and limit yourself to 1 to 2 drinks per occasion. Avoid sugary cocktails.
8. Use Sugar Substitutes in Moderation
Sugar substitutes like Splenda®, stevia, or aspartame can replace sugar but should be used moderately to avoid digestive discomfort.
Artificial sweeteners may also maintain sugar cravings, potentially increasing the desire for sweet foods.
Practical tip: Try various alternatives (e.g., stevia, erythritol) to find what works best for you. Limit use to 2–3 servings per day.
Loving Your Food is Key
The most important part of diabetes management is enjoying what you eat and being able to maintain these habits long-term. A registered dietitian with expertise in diabetes can help tailor these recommendations to your food preferences, making changes enjoyable and sustainable!
Final Word
Diabetes can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes—such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and mindful eating habits. Consult a nutritionist to receive personalized advice and take charge of your health.